Differences HOME and INDUSTRIAL compost
Packages, fabric moisturising masks, mobile phone cases, coffee capsules... The number of everyday objects that can be composted is growing. Some are compostable at home and others in an industrial environment. But what are the differences?

The answer is simple: a product that has been tested in the laboratory for compostability in a domestic environment can be added to the consumer's personal composter (in the garden or on the balcony for example). It will gradually degrade if mixed with the organic matter in the compost bin.
The same will happen if the consumer brings his/her waste to an industrial composter, as the conditions for decomposition of the product are more favourable there than in a domestic environment.
The opposite, however, is not true: a product that has been tested and validated for compostability in an industrial environment cannot automatically be composted in a domestic environment where the conditions for disintegration are less favourable (notably less heat). The product must therefore be disposed of either in household waste or taken to a composting centre (or, if the community accepts industrial compostable products as bio-waste, the consumer can include his/her waste in the collection).
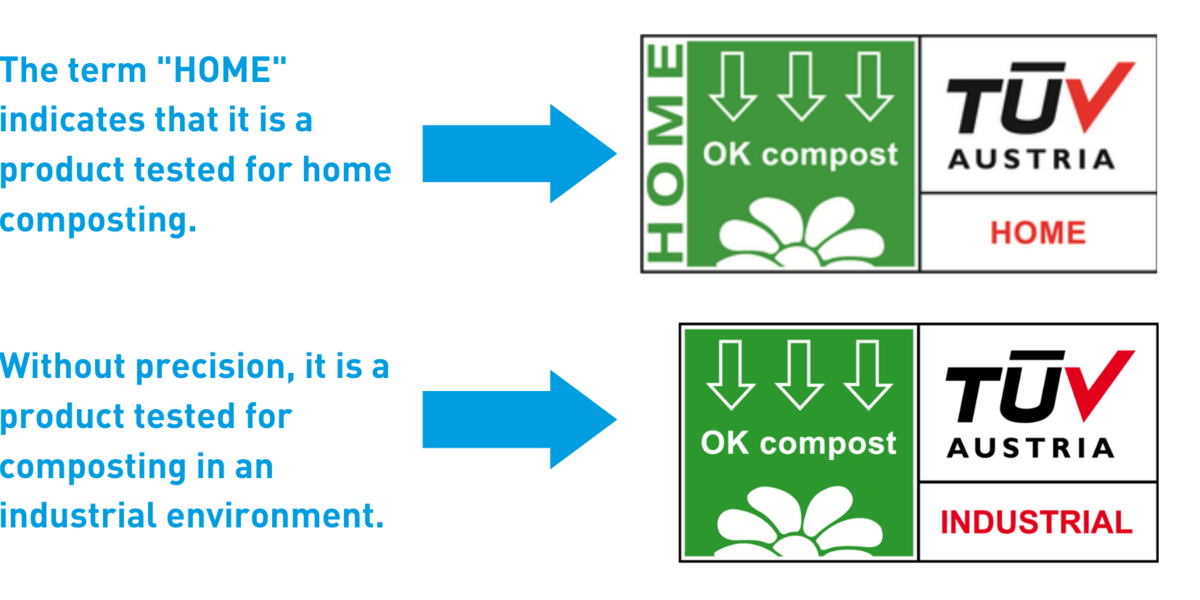
How do you know if a product is compostable in a domestic or industrial environment?
The logos on products must be self-explanatory and indicate the context in which the product will degrade.
The best-known logos in France are those of TÜV AUSTRIA. They are differentiated by their visuals.
Other certification bodies issue their own logos. This could be DIN CERTCO, for example. In all cases, these recognised logos are a guarantee of quality and compliance with the applicable standards.
It should be noted that the use of these known logos is not an obligation.
If the products have been tested according to the defined standards (see our article on the standards in force), the manufacturer can market a product that is "compostable" in the environment for which it has been tested by adding the corresponding mention or a visual of its own.
Please note, however, that in order to be labelled "compostable in a domestic environment" or "compostable in an industrial environment", the tests must be carried out in accordance with defined standards and by an independent laboratory.
About WESSLING:
WESSLING carries out compostability tests in its French laboratory, located in Isère. We are recognised by TÜV AUSTRIA and DIN CERTCO, two independent certification bodies that have recognised our skills.
Do you have further questions about compostability? Would you like to test a product?
Contact us today!
Your contact
- Frédéric Jeampierre
- +33 7 56 37 24 99
- frederic.jeampierre@wessling.fr